 Missing References In VBA
Missing References In VBA
This page describes what to do if references in VBA cannot be found.

There may be times, especially when copying a workbook from one machine to another, that the references for that VBA project
are not properly carried through to the new machine. This normally happens when your project is using a DLL that is not part
of the core set of DLLs that make up the VBA environment for Office.
A Reference in a VBA Project is a "pointer" to a type library or DLL file that defines various objects and entities and the
properties and methods of those entities. For example, the VBP Project for any Excel worksbook contains a reference to the
Excel "type library" which defines the objects and their properties and methods that make up Excel. The Excel library defines
things like Worksheets and Ranges. Each reference has a property called the GUID (Globally Unique IDentifier).
When a workbook is opened, Excel reads the GUID for each reference, looks in the System Registry for the GUID to find the
appropriate library that defines the objects and their methods and properties. When you transfer a workbook from one machine
to another, the DLL files and Type Libraries referenced by the VBA Project are not copied along with the workbook. Only the
pointers (the GUIDs) are transfered, and when the workbook is opened on the second machine, Excel tries to find the components
identified by those GUIDs. If the GUID isn't found on the target machine, or the file to which the GUID refers is not found,
you'll get the MISSING indicator in the References dialog.
There are four core references that must be in place for VBA to work at all in Excel. A fifth references is required if you are
user UserForms. These references are listed below:
- Visual Basic For Applications This is the library that defines the VBA language.
- Microsoft Excel Object Library This defines all of the elements of Excel.
- OLE Automation This specifies the types for linking and embedding documents and for automation of
other applications and the "plumbing" of the COM system that Excel uses to communicate with the outside world.
- Microsoft Office This defines things that are common to all Office programs such as Command Bars and
Command Bar controls.
- Microsoft Forms 2.0 This is required if you are using a User Form. This library defines things like the
user form and the controls that you can place on a form.
You can view the current reference set from the
Tools menu in VBA and selecting
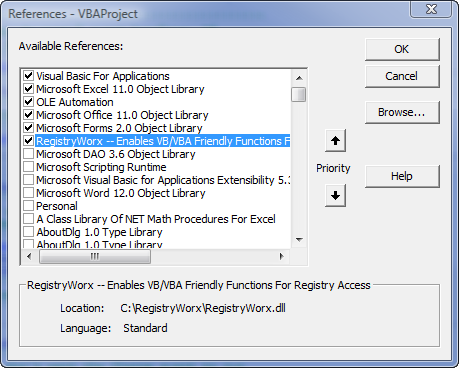
References. A typical reference
set is shown below on the left. If a reference required by the VB Project cannot be found, it is marked as
MISSING in the
References dialog. In the dialog below on the right, I renamed
the
RegistryWorx DLL to cause VBA to display that reference as missing.
A
References dialog with a missing reference is shown below on the right.
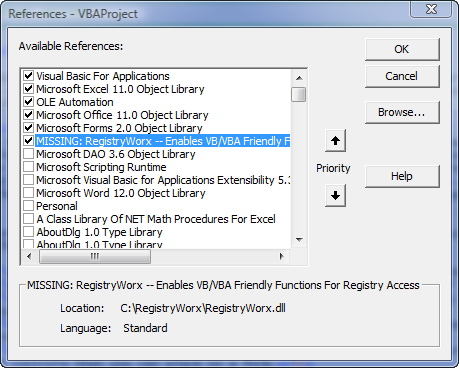
If there is a reference in the VB Project that refers to a library that VBA cannot find on the local machine, VBA marks that reference
as MISSING in the References dialog, as shown above on the right. A missing reference can cause bizarre
compiler messages when you compile the code or attempt to run the code. It might flag VBA objects (defined in the properly
referenced library for VBA) as unknown types. For example, it may flag the Instr method as not found,
even though the library that defines Instr is properly referenced. If a reference is missing,
the behavior of the compiler is erratic at best.

If a reference is marked as MISSING, you need to take some action to fix the problem. If the missing reference
is one of the core references listed above, you can try to have Excel fix the problem. First, you should try the Detect And Repair
option on the Help menu. After this has run, close Excel and reopen it and look at the References dialog in VBA. If
there are no missing references, then Detect And Repair worked successfully. If this doesn't fix the problem, close Excel,
go to the Windows Start menu, choose Run and enter the following and click OK.
"C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office\Excel.exe" /unregserver
Of course, your folder path to Excel.exe may be different. Once you have done this, repeat the process
but change /unregserver to /regserver. This causes Excel to delete all of its
System Registry key, and then restore them to the "factory defaults".
If this doesn't fix the problem, you'll need load the Office CD, run Setup.exe and tell the
Setup.exe to repair the Office application.
If the missing reference is not one of the core libraries, you first need to determine whether the DLL being referenced in necessary
to your application. Whether you need the reference depends on what your project does and what its external dependencies are. You can
uncheck the MISSING reference and then attempt to compile the project from the Debug menu. If you
do not get any compiler errors, then it is likely that the reference is not needed and you can leave it unchecked. If, on the other hand,
you get a compiler error message like User-defined type not defined, then you do need the reference for the project to work.
In this case, you can try a few things. Below the list of references in the References dialog, the full path name that is
associated with the missing reference is displayed. Determine if that file actually exists. If it does exist, close Excel, go to the
Windows Start menu, choose Run, and enter the following and press OK:
RegSvr32 "C:\folder\filename.dll" /u
where "C:\folder\filename.dll" is the fully qualified file name of the DLL file. Repeat this process but
omit the /u switch. If you get a message indicating success, reopen Excel, open the VBA Editor and see
if the reference is still marked as missing. If it is, uncheck it, then click the Browse button and navigate to the file that
you used in the RegSvr32 command above. This should properly add the reference to the file.
If you cannot find the file that is marked MISSING, there is not much you can do. If the DLL is from a third
party, you can re-install the component from the CD or Setup.exe program supplied by the vendor of the control or library. If you do
not have the CD or Setup.exe program for the library, contact the vendor for assistence. If that is unsuccessful, you can copy the
DLL file from the machine on which the program works to the new machine and then register the DLL with Windows using the
RegSvr32 commands as described above. (Note that while this last method may work and resolve the problem,
it may not be allowed by the license argreement to which you consented when you originally installed the control.)
If none of the steps above work, there is little else you can do. The workbook will be inoperable.
For other methods to diagnose and correct startup errors in Excel, see Startup Errors In Excel.
This page last updated: 27-October-2007