 FindAll Function
FindAll Function
This page describes VBA functions that can be used to find all the occurrences of a value
on a single worksheet or on multiple worksheets.

If you are looking for the FindAll.xla add-in, please go to the
FindAll Add-In page.
The Find method of the Range object is bit tricky to work with until you understand how it works. The logic
to find all of the cells that contain a searched-for value is more complicated than just calling Find and
FindNext.
In the course of examining the Find and FindNext methods, we will create a
function that returns a Range object that contains all the cells in which a searched-for string occurs.
You can download a module file containing all of the code on this page.
Suppose we have data in cells A1:A10 as shown below.
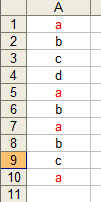 You might be tempted to write code like the
following to find occurrences of the value 'a'.
You might be tempted to write code like the
following to find occurrences of the value 'a'.
Dim FoundCell As Range
Set FoundCell = Range("A1:A10").Find(What:="a")
Do Until FoundCell Is Nothing
Debug.Print FoundCell.Address
Set FoundCell = Range("A1:A10").FindNext
Loop
Unfortunately, this will not work for several reasons. First, unless specified otherwise, the Find
method start searching after the the first cell, so the first cell found is A5 not
A1. Second, the FindNext method will continue to find
cell A5; as written, it won't really continue find the subsequent cells. To remedy this, we need to
specify which cell after which the search should look for a value. In the call to Find we need
to specify the last cell in A1:A10 so searching will begin at the end of the range and
loop back up to the top of the range. We can do this with code like the following (additonal code is shown in
yellow).
Dim FoundCell As Range
Dim LastCell As Range
With Range("A1:A10")
Set LastCell = .Cells(.Cells.Count)
End With
Set FoundCell = Range("A1:A10").Find(What:="a", After:=LastCell)
Do Until FoundCell Is Nothing
Debug.Print FoundCell.Address
Set FoundCell = Range("A1:A10").FindNext
Loop
With the After paramater set to the last cell of the range, the code will immediately loop back to the top
of the range and cell A1 is the first found cell. However, we still have a problem with the
FindNext method. On the first call to FindNext, the code will correctly find the next
occurrence in cell A5, but every subsequent call to FindNext will continue to
find cell A5. It won't really find the next cell. To fix this problem, we need to provide the
After parameter to FindNext. This is shown below:
Dim FoundCell As Range
Dim LastCell As Range
With Range("A1:A10")
Set LastCell = .Cells(.Cells.Count)
End With
Set FoundCell = Range("A1:A10").Find(what:="a", after:=LastCell)
Do Until FoundCell Is Nothing
Debug.Print FoundCell.Address
Set FoundCell = Range("A1:A10").FindNext(after:=FoundCell)
Loop
There is still one problem with this code. The
FindNext method will loop through the range, go from the end of
the range back to the top of the range and find all the occurrences again. Left unchecked, this will loop forever finding the same
values over and over again. Therefore, we need to create some type of escape conditional test to terminate the loop. We do this
by storing the address of the first found cell and then escaping out of the loop if
FoundCell.Address is
equal to that address. This tells us that
FindNext has looped form the bottom of the range back up
to the top of the range.
Dim FoundCell As Range
Dim LastCell As Range
Dim FirstAddr As String
With Range("A1:A10")
Set LastCell = .Cells(.Cells.Count)
End With
Set FoundCell = Range("A1:A10").Find(what:="a", after:=LastCell)
If Not FoundCell Is Nothing Then
FirstAddr = FoundCell.Address
End If
Do Until FoundCell Is Nothing
Debug.Print FoundCell.Address
Set FoundCell = Range("A1:A10").FindNext(after:=FoundCell)
If FoundCell.Address = FirstAddr Then
Exit Do
End If
Loop
Finally, we have code that will (1) return the found ranges in the correct order (top to bottom), (2) will properly use
FindNext to find the subsequent cells, and (3) will termiante the
FindNext
loop properly.

The FindAll procedure finds all occurrences of a value in a specified range and returns a Range object that
contains all of the cell in which the searched-for value was found. Moreover, it the ranges
that make up this range object are in the order you would be expect, upper-left cell to lower-right cell, in either by-row or
by-column order. Since FindAll returns a Range object, you can use a
For Each loop to iterate through the found cells.
The prototype of the FindAll function is as follows:
Function FindAll(SearchRange As Range, _
FindWhat As Variant, _
Optional LookIn As XlFindLookIn = xlValues, _
Optional LookAt As XlLookAt = xlWhole, _
Optional SearchOrder As XlSearchOrder = xlByRows, _
Optional MatchCase As Boolean = False, _
Optional BeginsWith As String = vbNullString, _
Optional EndsWith As String = vbNullString, _
Optional BeginEndCompare As VbCompareMethod = vbTextCompare) As Range
The parameters to FindAll are as follows. FindWhat is the value
to search for. LookIn indicates whether to look in cell values, cell formulas, or cell
comments. The default is cell values. LookAt indicates whether to look at the entire cell
(a match occurs only if the entire content of the cell matches FindWhat). The default is
match entire cell. SearchOrder indicates whether the search should proceed row-by-row or
column-by-column. The default is row-by-row. MatchCase indicates whether the text match is
case sensitice (MatchCase = True or case insensitive (MatchCase = False).
The default if False. BeginsWith is a string that indicates that a cell will match only if it begins with the string
specified in BeginsWith. EndsWith is a string that indicates that a
cell will match only if it ends with the string in EndsWith. The comparisons carried out
against BeginsWith and EndsWith are case sensitive if
BeginEndCompare is vbBinaryCompare. If BeginEndCompare
is vbTextCompare, the comparison is case-insensitive. The default is vbTextCompare.
If both BeginsWith and EndsWith are empty string, no tests of the
cell content are performed. If either or both BeginsWith or EndsWith are
not empty strings, the LookAt parameter is automatically changed to xlPart.
You can call the FindAll function with code like:
Sub TestFindAll()
Dim SearchRange As Range
Dim FindWhat As Variant
Dim FoundCells As Range
Dim FoundCell As Range
Set SearchRange = Range("A1:A10")
FindWhat = "a"
Set FoundCells = FindAll(SearchRange:=SearchRange, _
FindWhat:=FindWhat, _
LookIn:=xlValues, _
LookAt:=xlWhole, _
SearchOrder:=xlByColumns, _
MatchCase:=False, _
BeginsWith:=vbNullString, _
EndsWith:=vbNullString, _
BeginEndCompare:=vbTextCompare)
If FoundCells Is Nothing Then
Debug.Print "Value Not Found"
Else
For Each FoundCell In FoundCells
Debug.Print "Value Found In Cell: " & FoundCell.Address(False, False)
Next FoundCell
End If
End Sub

The code for FindAll is shown below. You can download a bas file containing
this function and the FindAllOnWorksheets function, described later.
Function FindAll(SearchRange As Range, _
FindWhat As Variant, _
Optional LookIn As XlFindLookIn = xlValues, _
Optional LookAt As XlLookAt = xlWhole, _
Optional SearchOrder As XlSearchOrder = xlByRows, _
Optional MatchCase As Boolean = False, _
Optional BeginsWith As String = vbNullString, _
Optional EndsWith As String = vbNullString, _
Optional BeginEndCompare As VbCompareMethod = vbTextCompare) As Range
Dim FoundCell As Range
Dim FirstFound As Range
Dim LastCell As Range
Dim ResultRange As Range
Dim XLookAt As XlLookAt
Dim Include As Boolean
Dim CompMode As VbCompareMethod
Dim Area As Range
Dim MaxRow As Long
Dim MaxCol As Long
Dim BeginB As Boolean
Dim EndB As Boolean
CompMode = BeginEndCompare
If BeginsWith <> vbNullString Or EndsWith <> vbNullString Then
XLookAt = xlPart
Else
XLookAt = LookAt
End If
For Each Area In SearchRange.Areas
With Area
If .Cells(.Cells.Count).Row > MaxRow Then
MaxRow = .Cells(.Cells.Count).Row
End If
If .Cells(.Cells.Count).Column > MaxCol Then
MaxCol = .Cells(.Cells.Count).Column
End If
End With
Next Area
Set LastCell = SearchRange.Worksheet.Cells(MaxRow, MaxCol)
On Error GoTo 0
Set FoundCell = SearchRange.Find(what:=FindWhat, _
after:=LastCell, _
LookIn:=LookIn, _
LookAt:=XLookAt, _
SearchOrder:=SearchOrder, _
MatchCase:=MatchCase)
If Not FoundCell Is Nothing Then
Set FirstFound = FoundCell
Do Until False
Include = False
If BeginsWith = vbNullString And EndsWith = vbNullString Then
Include = True
Else
If BeginsWith <> vbNullString Then
If StrComp(Left(FoundCell.Text, Len(BeginsWith)), BeginsWith, BeginEndCompare) = 0 Then
Include = True
End If
End If
If EndsWith <> vbNullString Then
If StrComp(Right(FoundCell.Text, Len(EndsWith)), EndsWith, BeginEndCompare) = 0 Then
Include = True
End If
End If
End If
If Include = True Then
If ResultRange Is Nothing Then
Set ResultRange = FoundCell
Else
Set ResultRange = Application.Union(ResultRange, FoundCell)
End If
End If
Set FoundCell = SearchRange.FindNext(after:=FoundCell)
If (FoundCell Is Nothing) Then
Exit Do
End If
If (FoundCell.Address = FirstFound.Address) Then
Exit Do
End If
Loop
End If
Set FindAll = ResultRange
End Function

VBA provides no built-in method for searching for a value in multiple worksheets. To do this, you need to loop through all of the
worksheets that you want to search and then do a regular search on each sheet. The FindAllOnWorksheets
automates this for you. It will search a range on any number of worksheets. It returns an array of Range objects, one element for
each sheet that was searched. If the value was not found on a sheet, that sheet's element in the returned array is
Nothing.
The prototype of the FindAllOnWorkshets function is shown below:
Function FindAllOnWorksheets(InWorkbook As Workbook, _
InWorksheets As Variant, _
SearchAddress As String, _
FindWhat As Variant, _
Optional LookIn As XlFindLookIn = xlValues, _
Optional LookAt As XlLookAt = xlWhole, _
Optional SearchOrder As XlSearchOrder = xlByRows, _
Optional MatchCase As Boolean = False, _
Optional BeginsWith As String = vbNullString, _
Optional EndsWith As String = vbNullString) As Variant
where InWorkbook is the workbook containing the sheets to be searched,
InWorksheets references the worksheets to be searched (see below), SearchAddress
is the address of the range on each sheet that is to be searched, and FindWhat is the value to search for.
The remaining properties control the search operation and have the same meanings and effects as the parameters to the
Find method of the Range object. See the help documentation for details about
these parameters.
The InWorksheet specifies what worksheet are to be searched. This parameter may be any of the following:
- Empty: Search all sheets in the workbook
- String: The name of a single worksheet to search.
- String: The names of the worksheets to search, with the names separated by a colon character (:)
- Object: A Worksheet object to search
- Array: An array of references to the worksheets to be searched. Each element of this array may be one of the the
following:
- String: The name of the worksheet to be searched
- Integer Or Long: The index number of the sheet within the workbook
- Object: A Worksheet object to search
The bulk of the code of the FindAllOnWorksheet function is to provide the widest possible range of options
for specifying what sheets to search.
The FindAllInWorksheets function requires the FindAll function described above,
so you should import the entire module into your project.
You can download a bas file containing this function and the
FindAll function.
You can call the FindAllOnWorksheets function with code like the following:
Sub TestFindAllOnWorksheets()
Dim FoundRanges As Variant
Dim FoundRange As Range
Dim FoundCell As Range
Dim S As String
Dim N As Long
Dim Found As Boolean
FoundRanges = FindAllOnWorksheets(InWorkbook:=ThisWorkbook, _
InWorksheets:="Sheet1:Sheet3", _
SearchAddress:="A1:C10", _
FindWhat:="a", _
LookIn:=xlValues, _
LookAt:=xlWhole, _
SearchOrder:=xlByRows, _
MatchCase:=False)
For N = LBound(FoundRanges) To UBound(FoundRanges)
If Not FoundRanges(N) Is Nothing Then
Found = True
For Each FoundCell In FoundRanges(N).Cells
S = S & FoundCell.Worksheet.Name & ": " & _
FoundCell.Address(False, False) & vbCrLf
Next FoundCell
End If
Next N
If Found = True Then
S = "Search Results: " & vbCrLf & S
Else
S = "Search Results: " & vbCrLf & "Not Found"
End If
MsgBox S
End Sub

The code for the FindAllOnWorksheets function is shown below:
Function FindAllOnWorksheets(InWorkbook As Workbook, _
InWorksheets As Variant, _
SearchAddress As String, _
FindWhat As Variant, _
Optional LookIn As XlFindLookIn = xlValues, _
Optional LookAt As XlLookAt = xlWhole, _
Optional SearchOrder As XlSearchOrder, _
Optional MatchCase As Boolean = False, _
Optional BeginsWith As String = vbNullString, _
Optional EndsWith As String = vbNullString, _
Optional BeginEndCompare As VbCompareMethod = vbTextCompare) As Variant
Dim WSArray() As String
Dim WS As Worksheet
Dim WB As Workbook
Dim ResultRange() As Range
Dim WSNdx As Long
Dim R As Range
Dim SearchRange As Range
Dim FoundRange As Range
Dim WSS As Variant
Dim N As Long
If InWorkbook Is Nothing Then
Set WB = ActiveWorkbook
Else
Set WB = InWorkbook
End If
If IsEmpty(InWorksheets) = True Then
With WB.Worksheets
ReDim WSArray(1 To .Count)
For WSNdx = 1 To .Count
WSArray(WSNdx) = .Item(WSNdx).Name
Next WSNdx
End With
Else
If IsObject(InWorksheets) = True Then
If TypeOf InWorksheets Is Excel.Worksheet Then
If StrComp(InWorksheets.Parent.Name, WB.Name, vbTextCompare) <> 0 Then
Exit Function
Else
ReDim WSArray(1 To 1)
WSArray(1) = InWorksheets.Name
End If
Else
End If
Else
If IsArray(InWorksheets) = True Then
ReDim WSArray(LBound(InWorksheets) To UBound(InWorksheets))
For WSNdx = LBound(InWorksheets) To UBound(InWorksheets)
If IsObject(InWorksheets(WSNdx)) = True Then
If TypeOf InWorksheets(WSNdx) Is Excel.Worksheet Then
WSArray(WSNdx) = InWorksheets(WSNdx).Name
Else
Exit Function
End If
Else
Select Case UCase(TypeName(InWorksheets(WSNdx)))
Case "LONG", "INTEGER"
Err.Clear
Set WS = WB.Worksheets(InWorksheets(WSNdx))
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
Exit Function
End If
WSArray(WSNdx) = WB.Worksheets(InWorksheets(WSNdx)).Name
Case "STRING"
Err.Clear
Set WS = WB.Worksheets(InWorksheets(WSNdx))
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
Exit Function
End If
WSArray(WSNdx) = InWorksheets(WSNdx)
End Select
End If
'WSArray(WSNdx) = InWorksheets(WSNdx)
Next WSNdx
Else
Select Case UCase(TypeName(InWorksheets))
Case "INTEGER", "LONG"
Err.Clear
Set WS = WB.Worksheets(InWorksheets)
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
Exit Function
Else
WSArray = Array(WB.Worksheets(InWorksheets).Name)
End If
Case "STRING"
If InStr(1, InWorksheets, ":", vbBinaryCompare) > 0 Then
WSS = Split(InWorksheets, ":")
Err.Clear
N = LBound(WSS)
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
Exit Function
End If
If LBound(WSS) > UBound(WSS) Then
Exit Function
End If
ReDim WSArray(LBound(WSS) To UBound(WSS))
For N = LBound(WSS) To UBound(WSS)
Err.Clear
Set WS = WB.Worksheets(WSS(N))
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
Exit Function
End If
WSArray(N) = WSS(N)
Next N
Else
Err.Clear
Set WS = WB.Worksheets(InWorksheets)
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
Exit Function
Else
WSArray = Array(InWorksheets)
End If
End If
End Select
End If
End If
End If
On Error Resume Next
For WSNdx = LBound(WSArray) To UBound(WSArray)
Err.Clear
Set WS = WB.Worksheets(WSArray(WSNdx))
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
Exit Function
End If
Err.Clear
Set R = WB.Worksheets(WSArray(WSNdx)).Range(SearchAddress)
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
Exit Function
End If
Next WSNdx
ReDim ResultRange(LBound(WSArray) To UBound(WSArray))
For WSNdx = LBound(WSArray) To UBound(WSArray)
Set WS = WB.Worksheets(WSArray(WSNdx))
Set SearchRange = WS.Range(SearchAddress)
Set FoundRange = FindAll(SearchRange:=SearchRange, _
FindWhat:=FindWhat, _
LookIn:=LookIn, LookAt:=LookAt, _
SearchOrder:=SearchOrder, _
MatchCase:=MatchCase, _
BeginsWith:=BeginsWith, _
EndsWith:=EndsWith, _
BeginEndCompare:=BeginEndCompare)
If FoundRange Is Nothing Then
Set ResultRange(WSNdx) = Nothing
Else
Set ResultRange(WSNdx) = FoundRange
End If
Next WSNdx
Set FindAllOnWorksheets = ResultRange
End Function
You can download a bas file containing the FindAll and
FindAllOnWorksheets functions. Since FindAllOnWorksheets required the
FindAll function, you should import the entire module into your project.
This page last updated: 5-January-2010